Annotation guidelines can be downloaded from Zenodo.
Cantemist train, development, test and background sets are already available at Zenodo
Corpus format
- Subtasks CANTEMIST-NER: Brat annotation format.

Figure 1. Example Brat annotation for Cantemist-Ner.
- CANTEMIST-NORM: Brat annotation format.
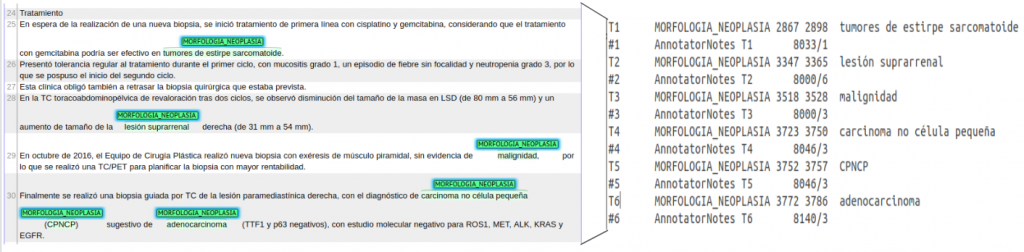
Figure 2. Example Brat annotation for Cantemist-Norm.
- Subtask CANTEMIST-CODING: CodiEsp format. We provide a single plain text file per clinical case and a tab-separated file with all the unique codes per clinical case (see Figure 3).
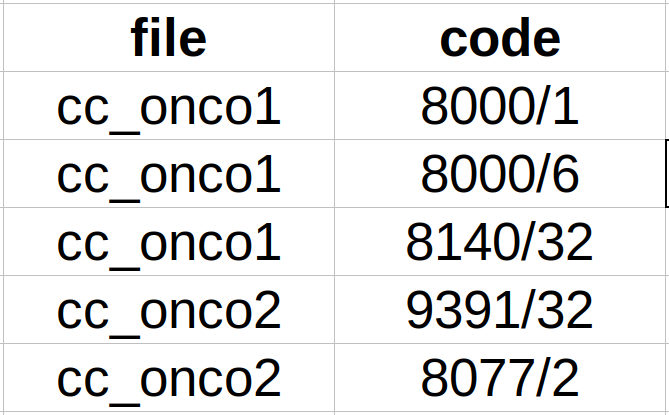
Figure 3. Example tab-separated file for Cantemist-Coding.
General information
For this task professional clinical coding experts have annotated a corpus of clinical cases in Spanish with eCIE-O-3.1 codes using the BRAT annotation tool following well-defined annotation guidelines adapted form the clinical coding recommendations published by the Spanish Ministry of Health, after several cycles of quality control and annotation consistency analysis before annotating the entire dataset. Figure 2 shows a screenshot of a sample manual annotation generated using the BRAT annotation tool.

Figure 2. Example BRAT annotation with labeled tumor morphology entity mention.
The CANTEMIST corpus consists of a collection of 3000 clinical cases that will be distributed in plain text in UTF8 encoding, where each clinical case would be stored as a single file. These clinical case reports were carefully selected to represent records reflecting as much as possible clinical narrative related to electronic clinical reports. Figure 3 illustrates an example text snippet corresponding to a short sample record.

Figure 3. Example plain text CANTEMIST corpus document
Additionally, we will also provide the annotation files comprising the character offsets of the tumor morphology entity mentions in TSV (tab-separated values) BRAT format together with their corresponding eCIE-O-3.1 code annotations.
The final corpus will be randomly split into three subsets: training, development and test. In the case of training and development sets, additionally, to the clinical cases, a TSV file will be released. It will contain one row per annotation. Each row will consist of the eCIE-O-3.1 code of the clinical case, a label indicating the category of the annotation, the annotation code and a reference to the text span that stimulated the annotation (the evidence).
In addition to the test set, a larger background set of clinical case documents will be released to make sure that participating teams will not be able to do manual corrections. In addition, the background set will become a silver standard of texts coded through automatic eCIE-O-3.1 code predictions returned by participating teams.
The goal of the CANTEMIST task is to develop automatic eCIE-O-3.1 clinical coding systems for Spanish medical texts. These systems should rely on the use of the CANTEMIST corpus, a high-quality Gold Standard synthetic clinical corpus of 3000 records based on a manual annotation process done by human clinical coding experts together with an inter-annotator agreement consistency analysis.
The CANTEMIST task can be approached as a named entity recognition and normalization task, but also as a multi-class text classification task. Participants are encouraged to either propose solutions in one of these directions or to combine both approaches. As well, novel approaches are welcomed.