Multilingual corpus & cross-mappings
Annotation guidelines will be available in Zenodo.
DISTEMIST training, test and background sets (including the multilingual corpus and cross-mappings) are available at Zenodo.
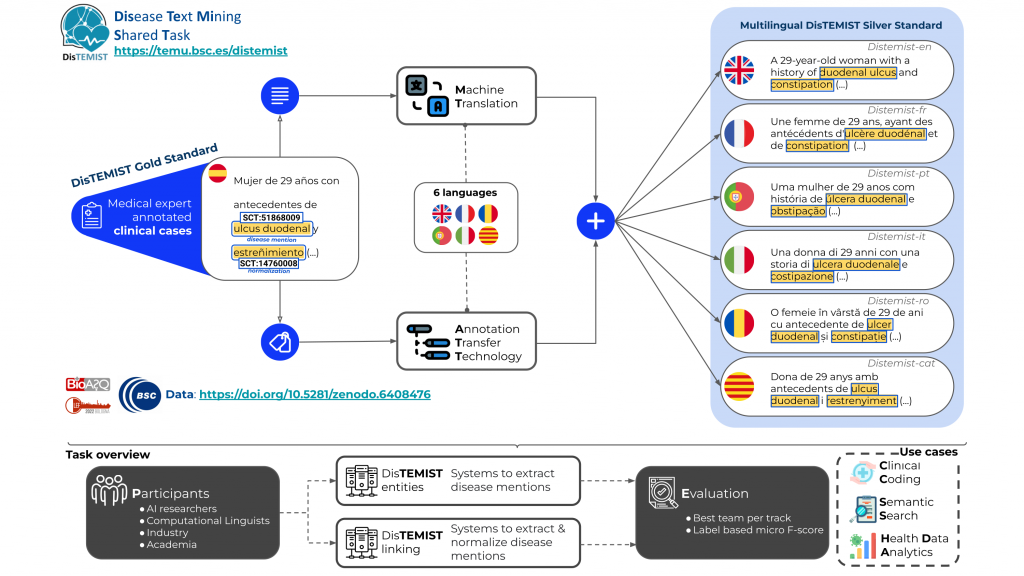
DISTEMIST Multilingual corpus
We have generated the annotated (and normalized to Snomed-CT) training and validation sets in 6 languages: English, Portuguese, Catalan, Italian, French, and Romanian. The process was:
- The text files were translated with a neural machine translation system.
- The annotations were translated with the same neural machine translation system.
- The translated annotations were transferred to the translated text files using an annotation transfer technology.
If you want to visualize the multilingual resources, check out this Brat server: https://temu.bsc.es/mDistemist/#/translations/
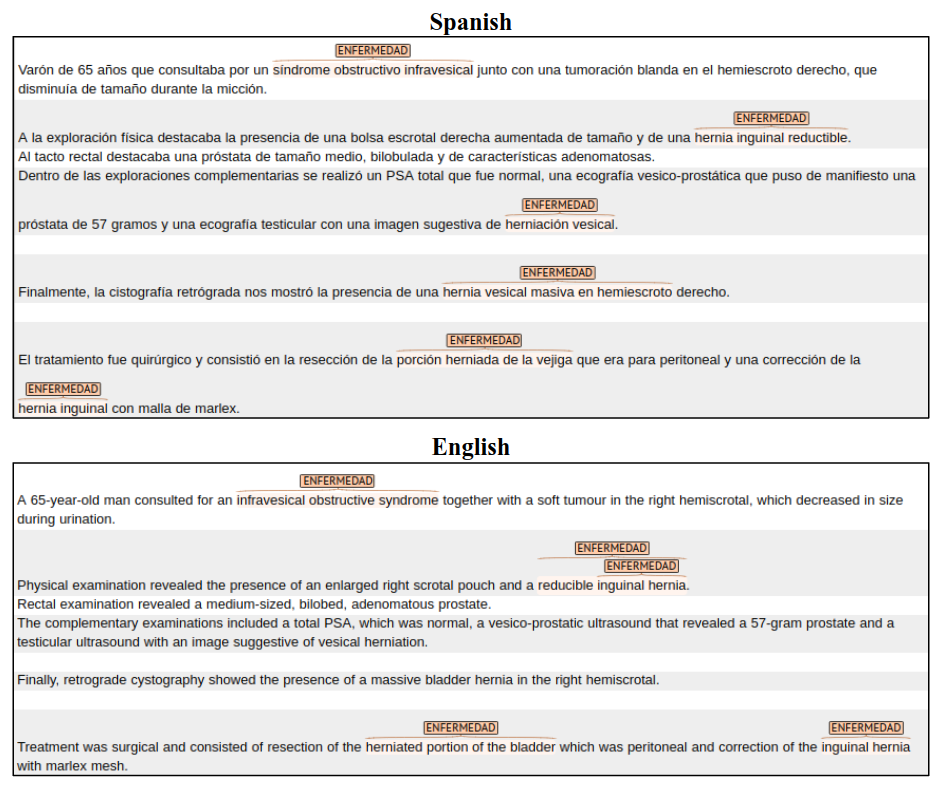
For instance, you can see the parallel annotations in English vs in French, or in Spanish (the gold standard) vs in Italian.
DISTEMIST cross-mappings
The DISTEMIST Gold Standard contains the mentions mapped to Snomed-CT.
In the DISTEMIST cross-mappings files we include the same entities as in DISTEMIST-linking but mapped to Snomed-CT, MeSH, ICD-10, HPO, and OMIM. The original mappings are manual and to Snomed-CT. The mappings to the other terminologies were done through the UMLS Metathesaurus.
Description of the Corpus
Annotation guidelines will be available in Zenodo.
DISTEMIST training, test and background set is available at Zenodo.
This page contains the following information:
Corpus format
DISTEMIST-entities. Annotations are stored tab-separated file with headers and 6 columns:
- filename: document name
- mark: identifier mention id
- label: mentions type (ENFERMEDAD)
- off0: starting position of the mention in the document
- off1: ending position of the mention in the document
- span: text span
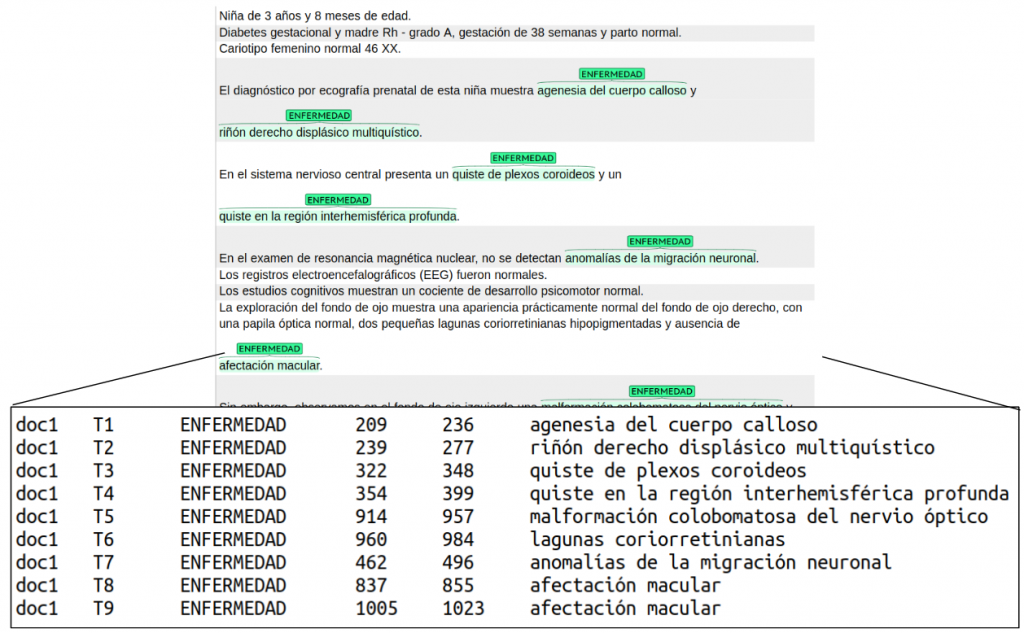
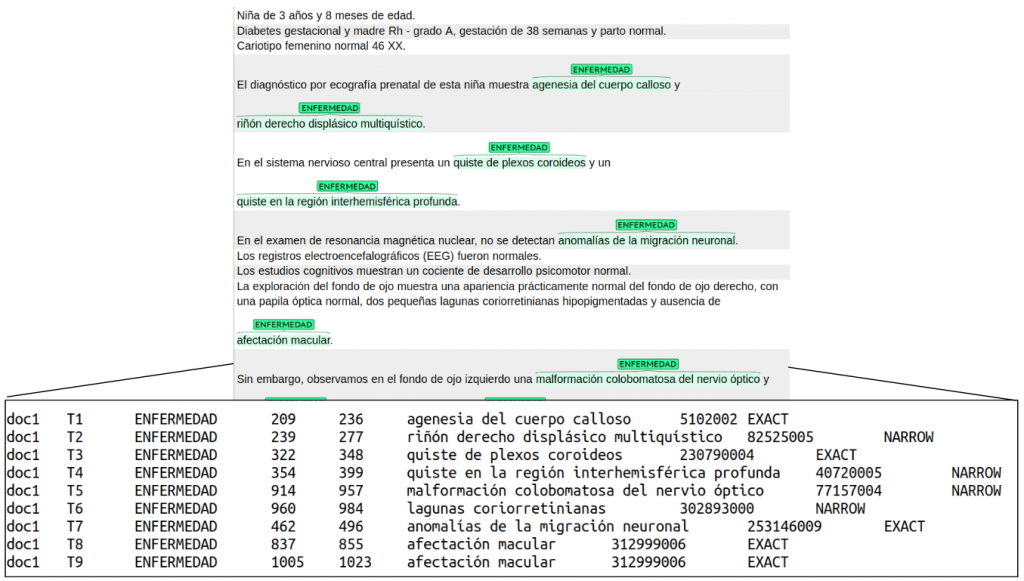
Figure 1. Example annotation for DISTEMIST-entitiesDISTEMIST-linking. Annotations are stored tab-separated file with headers and 8 columns: filename: document name
- mark: identifier mention id
- label: mentions type (ENFERMEDAD)
- off0: starting position of the mention in the document
- off1: ending position of the mention in the document
- span: text span
- codes: List of Snomed-CT concept codes linked to the mention. If there is more than one code associated with a mention, they will be concatenated by the symbol “+”.
- semantic relation: the relationship between the assigned code and the mention. It can be EXACT, when the code corresponds exactly with the mention, or NARROW, when the mention corresponds to a narrower concept than the Snomed-CT code. For instance, the concept “Chorioretinal lacunae” does not exist in Snomed-CT. Then, it is normalized to the Snomed-CT ID 302893000 (“Chorioretinal disorder”).
The raw clinical case documents are distributed in plain text in UTF8 encoding, where each clinical case would be stored as a single file.
General information
The DISTEMIST corpus is a collection of 1,000 clinical cases in Spanish from different medical specialties such as cardiology, oncology, otorhinolaryngology, dentistry, pediatrics, primary care, allergology, radiology, psychiatry, ophthalmology, and urology annotated with disease mentions. Each of the mentions in the corpus has been standardized using SNOMED-CT terminology.
All clinical case records derived from various databases were gathered in a first step, preprocessed and the actual clinical case section was extracted removing embedded figure references or citations. These records were classified manually using the MyMiner file labeling online application by a practicing oncologist and revised by a clinical documentalist in order to assure that these records were related to the medical domain and they resembled the kind of structure and content that is relevant to process clinical content. During this process, clinical cases from other fields like psychology, historical forensics, some very particular cases of epidemiology studies, or clinical case series not focused on a single patient/clinical case were removed. The final collection of 1000 clinical cases that make up the corpus had a total of 16504 sentences, with an average of 16.5 sentences per clinical case.
The disease mention annotation was done by clinical experts using the BRAT annotation tool following well-defined annotation guidelines, defined after several cycles of quality control and annotation consistency analysis before annotating the entire dataset.
The corpus was randomly split into two subsets: training and test set. The test set will be used for evaluation purposes of participating teams and will consist of a total of 250 records.
Datasets
Annotation guidelines will be available in Zenodo.
DISTEMIST training, test and background set is available at Zenodo.
See information about datasets for Sub-track Distemist-entities
See information about datasets for Sub-track Distemist – linking
Resources
DISTEMIST gazetteer
- DISTEMIST gazetteer: contains main terms and synonyms from the relevant branches of Snomed-CT for the grounding of disease mentions. Relevant for NER and Entity linking. Find it on Zenodo.
Evaluation Script
- Official evaluation script (beta version).
Word embeddings
- Spanish Medical Word Embeddings. Word embeddings generated from Spanish medical corpora. Download them from Zenodo.
It can be used as a building block for clinical NLP systems used in Spanish texts.
Baseline
Dictionary lookup based on Levenshtein distance. It looks for train and development annotations in the test set.
Linguistic Resources
- CUTEXT. See it on GitHub.
Medical term extraction tool.
It can be used to extract relevant medical terms from clinical cases. - SPACCC POS Tagger. See it on Zenodo.
Part Of Speech Tagger for Spanish medical domain corpus.
It can be used as a component of your system. - NegEx-MES. See it on Zenodo.
A system for negation detection in Spanish clinical texts based on NegEx algorithm.
It can be used as a component of your system. - Negation corpus. See it on GitHub
A Corpus of Negation and Uncertainty in Spanish Clinical Texts (and instructions to train the system). - AbreMES-X. See it on Zenodo.
Software used to generate the Spanish Medical Abbreviation DataBase. - AbreMES-DB. See it on Zenodo.
Spanish Medical Abbreviation DataBase.
It can be used to fine-tune your system. - MeSpEn Glossaries. See it on Zenodo.
Repository of bilingual medical glossaries made by professional translators.
It can be used to fine-tune your system.
Terminological Resources
- List of valid Snomed-CT codes. To be published